Background
Caching is a proven technique to boost application performance by reducing repetitive computations or expensive data fetches. Dot net offers several caching strategies to accommodate various scalability needs:
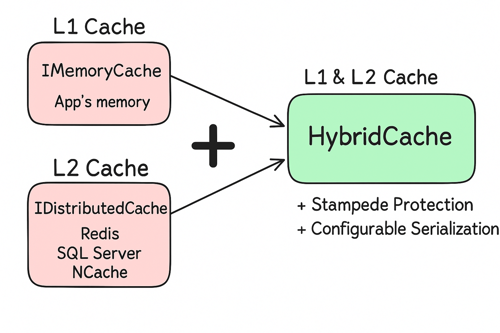
In-Memory Cache: Fast and simple. Stores data in memory on the current server. Ideal for single-instance applications.
Distributed Cache: Uses external sources like Redis or SQL Server to share cache across multiple servers. Ideal for cloud-native and scalable architectures.
With .NET 9, Microsoft introduces HybridCache —a powerful caching solution that combines the speed of in-memory cache with the scalability of distributed cache. It's a game-changer for developers who want performance and consistency without reinventing the wheel.
Key Features
Two-Level Caching: Combines memory speed with distributed reliability.
Stampede Protection: Prevents multiple threads from hitting the source simultaneously when data is missing.
Tag-Based Invalidation: Group cache entries by tags for easier bulk invalidation.
Flexible Serialization: Supports JSON, XML, and other formats.
Unified Expiration Control: Manage TTL and refresh policies centrally.
Advantages
Blazing Performance – Quickly serve data like API responses and user profiles from in-memory (L1) cache.
Reliable Fallback – If L1 cache is unavailable, fallback to distributed (L2) cache to avoid database hits.
Auto Syncing – Ensures consistency between local and distributed cache layers across all instances.
Unified Expiration Control – Centralized control over cache lifetimes and refresh policies.
Manual & Tag-Based Invalidation – Invalidate cache manually or in bulk using tags.
Caching API Responses – Reduce latency and load for frequently accessed endpoints.
Caching Paginated Results – Improve performance of list views and pagination-heavy data.
Caching User Profile Data – Minimize repeated DB access for user-specific data.
Manual Cache Invalidation – Clear specific or grouped entries when data updates occur.
Caching Aggregated Statistics – Speed up dashboard and analytics queries with precomputed data.
How to Add and Use HybridCache in a .NET App
These steps apply specifically to .NET 9 applications. HybridCache is part of Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.Hybrid namespace, and it integrates seamlessly into the dependency injection (DI) system used in .NET Core and .NET 9.
Install the NuGet Package
Use the following command to install the HybridCache package:
Install NuGet Packagedotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.Hybrid --version "9.0.0-preview.7.24406.2"Note: HybridCache is currently available in .NET 9 Preview. Ensure your SDK is updated accordingly
Configure HybridCache in the Program.cs
In yourProgram.cs or Startup.cs (depending on project type):HybridCache In Practicepublic class WeatherService { private readonly HybridCache _cache; private readonly IHttpClientFactory _httpClientFactory; public WeatherService(HybridCache cache, IHttpClientFactory httpClientFactory) { _cache = cache; _httpClientFactory = httpClientFactory; } public async Task<string> GetWeatherForecastAsync(string city) { return await _cache.GetOrCreateAsync( $"weather:{city}", async cancellationToken => { var client = _httpClientFactory.CreateClient(); var result = await client.GetStringAsync($"https://api.weather.com/{city}"); return result; }, cancellationToken: CancellationToken.None ); } }Using HybridCache in Your Code
Once registered in DI, you can inject and use HybridCache in any service or controller:HybridCache In Practicepublic class WeatherService { private readonly HybridCache _cache; private readonly IHttpClientFactory _httpClientFactory; public WeatherService(HybridCache cache, IHttpClientFactory httpClientFactory) { _cache = cache; _httpClientFactory = httpClientFactory; } public async Task<string> GetWeatherForecastAsync(string city) { return await _cache.GetOrCreateAsync( $"weather:{city}", async cancellationToken => { var client = _httpClientFactory.CreateClient(); var result = await client.GetStringAsync($"<a target="" data-router-slot="disabled" href="https://api.weather.com/{city}" type="external">https://api.weather.com/{city}</a>"); return result; }, cancellationToken: CancellationToken.None ); } }Here are key configuration options you can set globally:
MaximumPayloadBytes: The largest size allowed for any cached item (default is 1 MB). Items exceeding this size won’t be cached and will be logged.
MaximumKeyLength: The maximum length allowed for cache keys (default is 1024 characters). Keys longer than this won’t be stored and will be logged.
(Optional) Add Redis as a Distributed Store
If you want to back HybridCache with a distributed store like Redis, register it as follows:Program.csbuilder.Services.AddStackExchangeRedisCache(options => { options.Configuration = "your-redis-connection-string"; options.InstanceName = "your-redis-InstanceName-string:"; });This step is optional because HybridCache can operate using only the in-memory cache if desired.
After these steps, HybridCache is ready to be used in your application!
Implementation
Dummy API (Simulated external data source)
This simulates an API call to an external service. We’ll cache the results of this call using different strategies.Dummy Apipublic class DummyApi { private readonly HttpClient _httpClient = new HttpClient(); public async Task<string> FetchDataAsync(string key) { var response = await _httpClient.GetStringAsync("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/comments"); return response; } }In-Memory Cache Implementation
We first check the in-memory ConcurrentDictionary. If not found, fetch from API and store in cache.In-Memory Cachepublic async Task<string> GetAsync(string key) { if (_cache.TryGetValue(key, out var value)) return value; var data = await api.FetchDataAsync(key); _cache[key] = data; return data; }Redis Cache Implementation
We check Redis for the key. On miss, fetch from API and store back in Redis.Redis Cache Implementationpublic async Task<string> GetAsync(string key) { var cached = await redisDb.StringGetAsync(key); if (cached.HasValue) return cached; var data = await api.FetchDataAsync(key); await redisDb.StringSetAsync(key, data); return data; }Hybrid Cache Implementation
This uses HybridCache to combine local memory + Redis under the hood. Fallback logic is handled by the library.Hybrid Cache Implementationpublic async Task<string> GetAsync(string key) { return await _cache.GetOrCreateAsync( key, async cancel => await _api.FetchDataAsync(key), cancellationToken: CancellationToken.None ); }Benchmark Result
After running, here’s the performance comparison:

Hybrid Cache Benchmark
Summary
HybridCache combines L1 (in-memory) and L2 (distributed) caching for optimal performance and scalability.
Reduces database stress with stampede protection.
Easy to configure and integrates cleanly .
Ideal for both monoliths and microservices.
Delivers simplified caching with advanced features like tagging and serialization.
Related Reading: When it comes to speed and scalability in rate-limited environments, thread management often becomes a key aspect to be looked at - explore our Building Resilient C# Apps blog to know more about it.
References
Related Blogs

Building Resilient C# Apps
Avoiding Thread Starvation in Rate-Limited Environments

Vertical Slice Architecture In Modern Application Design
A modern approach that’s becoming popular is Vertical Slice Architecture.

Cursor vs Offset Pagination in EF Core with Benchmarks
Pagination is the technique of splitting a dataset into smaller chunks (pages) instead of retrieving everything at once.
